
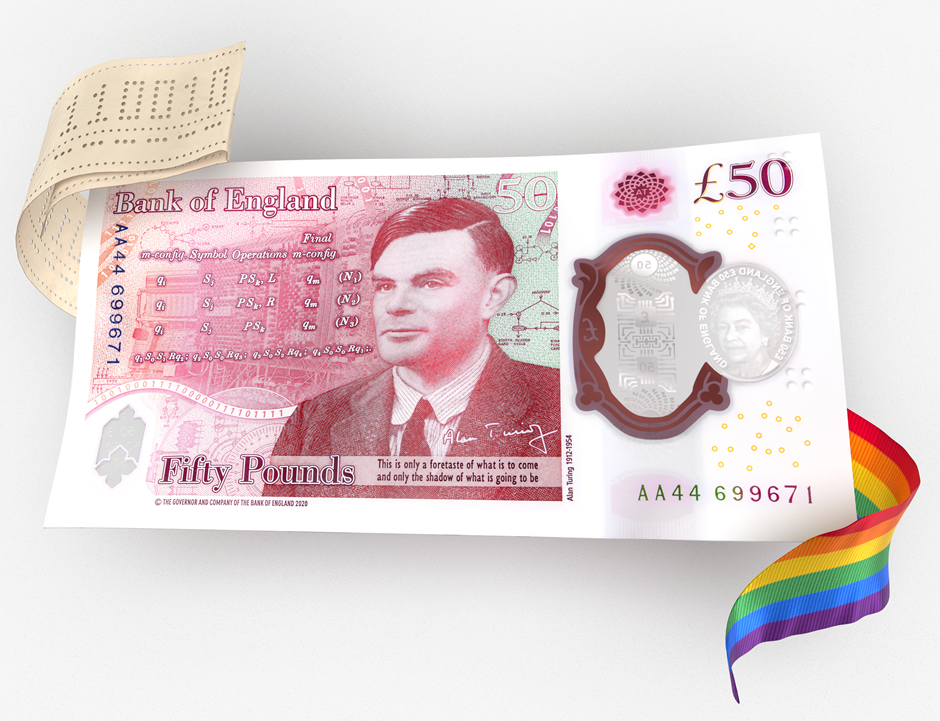
Bank of England governor Andrew Bailey has unveiled the design of the new £50 banknote featuring the scientist Alan Turing.
The polymer £50 will be issued for the first time on 23 June 2021, which coincides with Alan Turing’s birthday.

Access deeper industry intelligence
Experience unmatched clarity with a single platform that combines unique data, AI, and human expertise.
The new £50 note contains advanced security features, completing our most secure set of Bank of England polymer banknotes yet.
Like the £20, it also incorporates two windows and a two-colour foil, making it very difficult to counterfeit. There is also a hologram image which changes between the words ‘Fifty’ and ‘Pounds’ when tilting the note from side to side.
One of the benefits shared by all the polymer banknotes is that they last longer than paper notes and they stay in better condition during their use.

US Tariffs are shifting - will you react or anticipate?
Don’t let policy changes catch you off guard. Stay proactive with real-time data and expert analysis.
By GlobalDataThis note, like the polymer £10 and £20 will contain a tactile feature to help vision impaired people identify the denomination.
The polymer £50 note will join the Churchill £5, the Austen £10 and the Turner £20, meaning all Bank of England banknotes are now available in polymer.
The public will begin to see the new £50 from 23 June 2021 as the notes enter general circulation. The public can continue to use paper £50 notes as usual.
Notice will be given at least six months ahead of the date when the old paper £50 is withdrawn.
Who was Alan Turing?
Alan Mathison Turing OBE FRS (23 June 1912 – 7 June 1954) was an English mathematician, computer scientist, logician, cryptanalyst, philosopher, and theoretical biologist.
Computer science & artificial intelligence
Turing was highly influential in the development of theoretical computer science, providing a formalisation of the concepts of algorithm and computation with the Turing machine, which can be considered a model of a general-purpose computer.
Turing is widely considered to be the father of theoretical computer science and artificial intelligence.
Despite these accomplishments, he was never fully recognised in his home country, if only because much of his work was covered by the Official Secrets Act.
Code breaking
Alan Turing is perhaps best known for his codebreaking work during the Second World War.
During WW2, he was instrumental in breaking the German Enigma code, leading to Allied victory over Nazi Germany.
Biology
Although famous for his work on codebreaking and computing, Alan Turing is less well known for his discoveries in the field of biology.
Turing was a pioneer of morphogenesis, where he used mathematics to understand how natural patterns like the spiral formation of the seeds in a sunflower head, and the arrangement of spots on a leopard can form.







