
UK businesses have been hit with a sharp rise in taxes in the first Labour Party budget for 14 years.
The government has committed to fund a cash injection for the health service by borrowing more and by raising taxed.

Access deeper industry intelligence
Experience unmatched clarity with a single platform that combines unique data, AI, and human expertise.
If the government is to be believed, it is a budget to boost growth. Gilbert Verdian, founder and CEO of Quant, agrees and his comments are included below. Nigel Green, CEO of deVere Group, has a rather different take. A number of government critics argue that any boost to growth will be short-lived.
Capital gains is up, employers national insurance contributions are raised and stamp duty rises on second homes.
RBI has canvassed opinion from a number of industry experts. Opinions are listed in alphabetical order by commentator. A number of common themes emerge, including relief that the threatened tax hikes were not worse and at least some agreement that the budget now provides a degree of certainty and stability.
Simon Allister, head of wealth planning, LGT Wealth Management
Tax was once considered one of life’s two certainties. But the chancellor seems aware that this is no longer the case for the internationally mobile wealthy, with multiple references today to maintaining the UK’s “competitiveness” against low-or-no tax jurisdictions.
US Tariffs are shifting - will you react or anticipate?
Don’t let policy changes catch you off guard. Stay proactive with real-time data and expert analysis.
By GlobalDataThere remains little granular detail around the abolition of the non-dom regime, which is disappointing given April 2025 is fast approaching. Taken in isolation, the changes look palatable for private clients relative to recent rampant speculation. That said, a sizeable minority will be significantly impacted. The impact on family businesses and those with significant pensions savings will be profound and it remains to be seen what the knock on impact will be on the government’s optimistic growth objectives.
Ravi Anand, Managing Director, ThinCats
There are many takeaways from today’s Budget, however, the big question remains, where is the growth going to come from? The OBR’s forecast reflects a stagnant economy, anaemic at best.
As a lender to mid-sized businesses that are looking to growth, acquire and expand, there are some areas that are welcome. I think for most business owners, a sense of stability, albeit at a cost, will provide an ability to finally forward plan.
We knew a CGT increase was coming and in the grand scheme of things, the increase ‘walked the line’ of incentivising to remain an owner or sell. There will be a natural increase in activity in M&A with some businesses looking to get ahead of this, but I don’t foresee a huge surge in activity. Retaining the Business Asset Disposal Relief is welcome too, but one consideration from the changes to business property relief is that we may see family-owned businesses changing hands because the incentives will no longer be in place.
More generally, certainty on corporation tax is welcome and initiatives to improve infrastructure in areas such as transport and carbon capture as well as regional funds are good things and will help the economy, but they certainly won’t lead to short term growth.
For all but particularly growth businesses, the NICs increases will be hugely frustrating but are of no surprise given the recent headlines. It will ultimately lead to higher costs for end customers and some lower recruitment.
While there aren’t many supporters of non-doms among the general public, I think in the medium term it will likely impact wealth creation. These are the unintended consequences of these policies.
Overall, the Chancellor walked the line and, in many ways, it felt quite Conservative with some Labour giveaways to lower earners. Notwithstanding, for businesses, it could have been worse, and most are probably breathing a sigh of relief.
Russell Andrews, head of wealth & asset management EMEA, FIS
The host of new tax changes in today’s budget will no doubt be causing high levels of stress for investing Brits. Updates, like the rise in capital gains tax, will be leaving them wondering how their portfolios and finances will be impacted. Wealth and asset managers should be on hand at this time to provide much needed advice and clarity. This could involve proactively reaching out to clients, helping them fully understand the implications of the budget, as well as helping them reassess their planning with long-term goals in mind. Additionally, now is the time to help prevent any ill-advised reactionary decisions.
This should be a straightforward task for the wealth and asset management industry. The changes in today’s budget have been expected for a few weeks, meaning managers should already be well positioned to advise customers, as well as reassure them that plans have been made to ensure their long-term goals have been kept on track.
Mark Ashbridge, Managing Director, Ashbridge Partners
A sensible and balanced budget focused on economic growth and tax revenue growth.
We were expecting significant tax raising measures and this is what we have got. Undoubtedly, the prospect of interest rates falling as far or as fast as the market has considered might be possible earlier in the year looks less likely given the spending and inflationary pressures coming from wage increases. That said, interest rates should continue a steady decline in the medium term.
Our assessment of today’s announcements is that bank finance will become even more important for families and businesses as they navigate the additional hurdles imposed by the restriction of Inheritance Tax (IHT) Relief’s, increase in Capital Gains Tax (CGT) and bringing Pensions into the IHT net. For example, a business owner may choose to raise finance against their business or its assets to transfer wealth to the next generation whilst retaining ownership and control of the business itself until a later date.
Under the current regime they wouldn’t need to consider this for IHT purposes because the business should transfer with 100% Business Property Relief (BPR) on death.
Similarly, individuals with large pension pots will no longer receive the IHT protection of the pension wrapper and so more people’s estates will be brought into the IHT net. This is likely to result in an increased take up of lifetime mortgages for pensioners where they can raise mortgages against their own homes and transfer the monies to the next generation. In short, there will be a much greater focus on IHT planning for more people than ever before and bank finance can plan a key role in this.
The budget measures are likely to generate activity, change and innovation, all of which should be positive for growth. Finance will be an increasingly important part of this next phase of economic growth both for businesses and individuals.
Andy Butcher, Branch Principal & Chartered Financial Planner, Raymond James Investment Services
Capital gains tax hikes ensure investing remains a rich man’s game
In today’s Budget, Rachel Reeves spoke at length about the importance of incentivising investment, wealth creation and economic growth, but there is a risk that the hikes to CGT announced today will dissuade Britons from investing in the long term. These changes are as predicted, but it’s disappointing an increase in the allowance isn’t forthcoming – this would encourage smaller investors and remove the burden of completing a tax return for relatively modest gains.
While the UK still has the lowest CGT rates of any European G7 economy, these costs will ensure individuals will have to pay more for the money they make and could put off people who were considering starting in investing. In a country where investing has long been understood as a rich man’s game, there is a danger today’s measures will further this fate.
State pension triple lock locked down, while employer NI contributions increase
The increase in employer national insurance contributions to 15% increases the burden on business owners by £800 per employee on full-time minimum wage. Thus, the increase in employers’ allowance will be most welcome for small businesses, though this will matter most for firms with five employees or less.
Encouraging saving for retirement must remain a priority for the Labour government. This change, as well as the reduction of the secondary threshold to £5,000, may impact short-term wage growth and possibly push employers to pull back on their pension contributions and schemes beyond the minimum described by the auto-enrolment regime, ultimately harming savers.
Inheritance tax threshold frozen until 2030, while inherited pensions now subject to tax
The Chancellor’s decisions on the inheritance tax threshold freeze and taxing inherited pensions, paired with increases to capital gains tax, mean that more estates are now liable to pay inheritance tax under the current rules, as inheritance tax bills have essentially increased over the past 15 years with asset price growth. Further increases to the inheritance tax regime will be harmful to younger generations, who will bear the brunt of double taxation on assets. Younger generations may also be unlikely to build large pension pots during their careers, due to allowance restrictions and the high cost of living, making this a further deterrent to savings.
Jessica Cath, Financial Crime Partner at Thistle Initiatives
The crackdown on welfare scammers announced in today’s budget demonstrates that reducing fraud is a clear priority for the new Labour government. It’s great to hear that innovative methods are being introduced to prevent this kind of illegal activity, along with new legal powers to stamp out fraudsters. This should serve as a message to all industries that the fight against financial crime is being taken seriously. Hopefully this is a step towards a more agile, responsive, and effective system for combating financial crime across the UK. In my opinion, to make this even more effective in the long-term, we need to see an ongoing, collaborative approach between the government, financial institutions, regulators and tech firms.
Theo Chatha, Chief Financial Officer, Bibby Financial Services
The new government came into power on a mandate set to support SMEs. But this budget fails to provide them with the support they need to succeed – and will even harm their growth.
Although the Employment Allowance did show recognition of the needs of the smallest businesses, an increase in employer national insurance payments still presents a real risk to SMEs. Many are already struggling with high costs and thin margins, so making employment more expensive could result in an immediate cashflow crisis. As a knock-on effect, we could see investment levels, growth ambitions and job creation all damaged as a result.
A rise in capital gains tax also discourages the entrepreneurial spirit the UK economy desperately needs. We’ve already seen the consequences of this. According to official figures, more than 1,600 company directors have closed their businesses’ doors since the start of October – by far the highest number of closures this year and more than double the amount for the whole of last October.
With today’s budget, the government has not made good on its promises to SMEs. Looking ahead, it must recognise not just their importance to the economy, but also their fragility. For many SMEs, just a few unexpected or high costs disrupt a precious balance and throw their future into doubt.
Miles Celic, Chief Executive Officer, TheCityUK
The Chancellor has fired the starting gun to deliver the government’s priorities over the next four years. Driving growth and investment remains the key challenge here in the UK. Our services sector is central to addressing this challenge, with financial and related professional services in particular a key part of the tool kit to deliver nationwide growth. The Chancellor has taken a broadly balanced approach on tax, sought to further bolster devolution and set out some positive measures to attract investment – but the detail behind the headlines is key. It is vital that these are all addressed through a lens of long-term international competitiveness. We urge the government to consult closely and swiftly with industry and we look forward to partnering with them to delivering the growth this country needs.
Greg Cox, CEO, Quint Group
Bluntly, the new Capital Gains Tax structure won’t help to inspire entrepreneurs to take risks and build companies and will make attracting investment more challenging, even while maintaining the business asset disposal relief. Entrepreneurship involves a lot of risk, which needs to be rewarded relative to taking the more typical path of full-time employment and job security. While the UK remains one of the world’s top fintech hubs, with a thriving ecosystem and remarkable talent base, today’s hikes will mean some entrepreneurs will think longer and harder about building a company and firms will need to keep finding creative, sustainable ways to grow in yet more adverse economic conditions.
That being said, many of today’s most successful companies emerged in challenging times. A tough investment landscape can inspire founders to prioritise lean, high-impact strategies and embrace risk with confidence. If anything, times like these bring forward bold ideas that might not emerge otherwise. The UK’s fintech landscape has a proven track record, and the opportunities for those ready to innovate and commit to their vision are as promising as ever.
Scott Dawson, CEO, DECTA
It was not as bad as expected for small to medium businesses. The focus on growth and investments is promising, though many of the intended changes may still put pressure on both consumers and businesses. The government’s tax hikes were undoubtedly intended to address the nation’s debt and inflationary pressures and, as with any government, the hardest decisions tend to be made in the first budget.
That being said, the surge in National Insurance Tax will have the unintended consequence of putting businesses under pressure, causing investors to shy away from the UK. This could undo so much progress the sector has clawed back following a tough five years. A large part of that progress is customer goodwill – companies live or die on whether their customers trust them, and in tough economic conditions those companies are going to be forced to compromise.
When this ‘rot economy’ reaches the payments industry, companies will need to change their business models to stay afloat. That will mean cutting back on the services that they can provide, being more conservative with their risk profile, avoiding innovative new technology and, as always, raising prices.
What we need to avoid is a world in which merchants can’t trust payments companies and consumers can’t trust the entire payments ecosystem. – which is more likely if a lack of investment makes such technologies complex and opaque.
John Dentry, Product Owner of the Current Account Switch Service at Pay.UK
The Autumn Budget is always an important time for the banking market. While some will be disappointed in the changes made, the foundations on which Labour will build their economy have been laid. The banking market will now adjust.
However, the market is resilient, and major fiscal events often lead to a more competitive landscape as the banks find their place in a new status quo. We’ve seen this in action across the last year, where switching levels have remained consistently high, with consumers increasingly willing to drop their long-standing partners to opt for an alternative that better suits their needs.
Switching is a fundamental tenant of a healthy banking ecosystem, and the ability to easily move between providers protects consumers, encourages innovation, and promotes competition. Lower base rates from the central banks are already driving innovation as institutions compete for customers without the use of eye-catching high-interest-rate savings accounts. Now that we’re past the budget, this competition is set to heat up.
Laurent Descout, co-founder, CEO of Neo
It’s disappointing to see the Chancellor moving forward with the increase in Capital Gains Tax, as this risks undercutting vital support for start-ups at a time when they need it most. This coupled with the national insurance hike represents a significant blow to businesses. Such moves discourage essential investment in start-ups, threatening their growth trajectory, IPO prospects and the jobs they create.
The UK should be fostering a pro-growth environment, especially given the recent spike in insolvencies and this tax increase feels like a step in the wrong direction for the business community.
Alastair Douglas, CEO, TotallyMoney
The 6.7% increase to the National Living Wage will put an extra £1,400 a year into the pocket of the typical person working 37.5 hours per week on the minimum wage. Which will be welcomed by lower earners, and hopefully ease some of the pressure on their finances.
But an employers’ NIC contributions hike will no doubt impact businesses, and especially the UK’s 5.5m SMEs. And it won’t just have an effect on their ability to offer pay rises in the new year, but to also improve staff benefits. And while the freeze income tax thresholds won’t be extended, it’s not moving any sooner, so it remains a stealth tax on everyday working people.
Today’s Budget also makes things more difficult for the UK’s tech industry, which is already facing challenges as a result of the economy and high interest rates. Over the past year, the Prime Minister has said he’ll show support — but actions speak louder than words, and we need to see a plan for growth.
Fintech in particular has a strong role to play in helping people get their finances back on track after the past few years. And the government needs to work with innovative firms to help fix the financial services, so the people it serves can start moving forwards.
Nigel Green, CEO, deVere Group
The Budget has delivered a stark message: tax hard, balance the books – but brace for an economic scar as talent and investment flood out.
These new measures are a clear disincentive to live, work, and invest in the UK. We’re already seeing a surge in interest as individuals and families look to secure their financial futures elsewhere.
This is not a time to wait. Now, more than ever, proactive wealth management is essential. Strategies such as leveraging tax-efficient vehicles, rebalancing portfolios, and planning inheritance early can help mitigate the impact of these changes.
The potential exodus of top talent and wealth could leave lasting scars on Britain’s economy, deterring future investors and undermining our global reputation as a hub for business and prosperity.
By effectively imposing a jobs tax, the Budget threatens to stifle hiring and curtail wage growth at a critical time. Employers facing higher payroll taxes are likely to cut back on recruitment or shift investment to automation, undermining job creation when the economy needs it most.
This Budget is more than just numbers – it’s a message that hard work and entrepreneurial success are being penalized. The government is not just taxing wealth but actively driving it away.
The Budget’s approach risks alienating expats who have long contributed to the UK economy, potentially driving them to re-evaluate their financial ties to the country.
Furthermore, the UK has long benefited from the economic contributions of non-doms, whose direct and indirect investments and business activities have been integral to the nation’s prosperity.
Additionally, the potential decline in the UK’s reputation as a tax-friendly hub may dissuade future investors and entrepreneurs from considering the country as their base of operations.
The allure of the non-dom tax status has been a pivotal factor in attracting international talent and creating a dynamic business environment.
Its removal is likely to signal a shift in the global perception of the UK as a favourable destination for wealth creation and business development.
Waiting for the dust to settle on this Budget could mean missing crucial opportunities to safeguard financial stability,” concludes the deVere CEO.
The reality is clear: this Budget is not just a short-term fiscal fix – it has far-reaching implications that will reshape the landscape for UK wealth, talent, and investment for years to come.
Brendan Harper, Head of HNW Technical Services, Utmost International
The changes confirmed by the Chancellor to the Resident Non-Domicile Regime brings months of uncertainty for UK resident non-domiciled individuals to an end.
With the scrapping of the regime, if non-domiciled individuals decide they want to live in the UK past four years they will need a long-term solution and alternative strategies to manage and protect their wealth effectively. For many, they may need to think beyond establishing trusts in order to shelter offshore income and gains for the long-term and to protect their estates from inheritance tax.
We suspect that after this announcement we will continue to hear clients talk about making plans to move to other jurisdictions such as Portugal, the UAE and Monaco where we have seen the highest levels of interest this year.
High-Net Worth individuals and their intermediaries now have certainty to take stock of the reforms and begin adjusting their financial plans accordingly.
Simon Harrington, Head of Public Affairs at PIMFA
Savers and investors will draw little consolation from the fact that measures announced in the Budget by the Chancellor today could have been worse.
We accept that the Chancellor has sought not to place a burden on working people (however this government chooses to define them), but in targeting Capital Gains Tax (CGT) in particular, this government risks stymying the very investment it seeks to stimulate economic growth. The government’s desire to utilise capital from pension funds to aid this has been much discussed, and we urge them not to needlessly erect further barriers for retail investors who can also play a crucial role in delivering growth.
Whilst we welcome the government’s extension of the inheritance tax threshold, the decision to change reliefs associated with it as well as the decision to bring pensions in scope will impact the effectiveness of people’s financial plans across the country and – in some cases, it may introduce doubts about the value of previous estate planning advice – specifically advice related to pensions. The value of financial advice is the certainty of outcome it can provide, and the confidence consumers can draw from that as a result. Constant tinkering with this regime diminishes the perceived value of holistic financial planning in particular.
Going forward, the Government should prioritise stability over future changes. We have been very clear that the government should adopt a taxation roadmap for personal taxation similar to the approach outlined for businesses in this Budget. Doing so would be enormously helpful and reassure savers and investors who need the confidence to know how their wealth will be treated both in accumulation and decumulation.
Simon Heath, Managing Partner, Heligan Group
Labour’s first budget since 2009 looks like Robin Hood on the tin, but Christmas Grinch under the skin.
With National Insurance contributions increasing at the same time as lowering the threshold at which companies pay from £9,100 to £5,000, employers are staring down the barrel of an 8-10% increase in staffing costs. This will be felt most widely in our supply chains; somebody will need to foot the bill, likely the consumer in their shopping baskets.
‘Robbing Peter to pay Paul’
Of course, the irony is that the higher the cost of labour, the smaller the profit margin and, therefore, the smaller the Corporation Tax taken by the government. This is a classic example of robbing Peter to pay Paul.
Minimum wage workers, especially in thin profit margin industries, will also need to hope they don’t lose their current job because businesses in these sectors will be faced with the decision to either cut staff or increase their prices.
Regardless of their decision, there’s likely to be a significant recruitment drop-off in most industries at a time when many companies are going to be looking to cut staff to balance the books.
Potential rise in unemployment among the most financially vulnerable
This leaves me concerned about a looming unemployment crisis for some of the most financially vulnerable people in the UK.
For a budget that claimed to be focussed on “invest, invest, invest”, I fear businesses and High Net Worths might roll back on investment when the AIM market is at its lowest point since 2001. With carried interest increased to 32% and CGT ramped up to 24%, private equity, a significant proportion of M&A deals, will need to reassess its position in the market as, ultimately, poor returns for the general partner. This will likely reduce company valuation parameters to compensate for the offshoot being lower CGT collection from lower pricing.
Regarding CGT, the increase was more moderate than most were expecting, likely to avoid spooking the M&A market in the short-term, an area which I think will remain mostly unchanged by this budget. In the long term, I believe this increase was more significant in signposting the direction of travel for CGT; I think we’ll see a steady increase over the next 5-10 years to move it towards harmonisation with dividend and income tax at around 40-45%.
Rachel Reeves was desperate for this to be the ‘People’s Budget’, but unfortunately, I’m not convinced this budget will have the intended impact. I hope I’m wrong.
Marion King, Chair and Trustee of Open Banking Ltd
We are encouraged to see the importance of data threaded throughout the Budget, with SME access to finance, an open data scheme for road fuel prices, and the reaffirmed role of DSIT as the digital centre of government.
Along with the Data Use and Access (DUA) Bill, now before Parliament, it is clear there is a strong commitment to furthering the UK’s leadership in data innovation and regulatory frameworks.
Open banking has already empowered millions of consumers and thousands of small businesses, facilitated efficient tax collection for HMRC to the sum of £30bn, and contributed billions to the UK economy. Building on this success, the proposed support for smart data schemes across a range of economic sectors will lay the groundwork for a smart data economy that benefits businesses, public services, and consumers.
The UK has laid a strong foundation for smart data through its approach to open banking, and by harnessing its potential, we can secure the UK’s status as a leader in digital innovation while delivering long-term economic growth.
James Klein, Corporate Partner, Spencer West LLP
The Capital Gains Tax (CGT) rate on carried interest will indeed be increasing from 28% to 32% from April 2025 from 28% to 32% (which is envisaged to be an interim step) as the Government seeks in its view to better reflect the economic characteristics and the associated level of risk being assumed by fund managers who receive it. Additional reforms are planned from April 2026 in order for the specific rules for carried interest are “simpler fairer and better targeted”. The advantage of this delay before additional reforms are introduced allows for some form of consultation during the interim period.
Certainly, the rise could have been larger – the sector is crucial to UK business and its need for private investment / growth capital and larger rises could have driven managers overseas. Others will undoubtedly reflect on the impact on fund managers and those working in the investment management industry and the need for those individuals (some 3,000+ in the UK) to bear the higher tax liability on their carried interest payments as well as the fact that the higher rate might deter new investments and delay new ones which would negatively impact investment into scaling UK businesses.
Silvija Krupena, Director of the Financial Intelligence Unit, RedCompass Labs
I’m disappointed there was no mention of plans to hold social media and technology firms accountable for the fraud that starts on their platforms. True change requires a united front across social media and technology platforms, banks, regulators, and law enforcement.
The Payment Systems Regulator’s recent new rules may protect consumers from financial loss, but they neither stop fraud nor solve the underlying problem. It’s time for the government to step up and realise that the onus should not be solely on banks and payment providers when it comes to stopping fraud.
The focus must shift to stopping fraud before it happens. And this is where firms like Meta must step up. Much of this fraud begins on platforms like Facebook and Instagram. But what is the government doing to urge these platforms to clamp down on fraud?
Gregory Marchat, Partner, Group head of financial services advisory, Forvis Mazars
The industry has consistently raised the negative impact of heavy regulation and high taxes on investment in the UK’s financial services sector. There is a clear demand for fiscal and regulatory reforms which deliver stability, enhance competitiveness, and demonstrate a commitment to the long-term potential of the sector. The budget was seen as an opportunity to cut through the fiscal uncertainty. Surprisingly, there were no specific mention of the financial sector in the budget – aside potential (yet limited) indirect impacts of some of the measures being implemented.
Now that the budget is out, it is important to continue addressing regulatory ambiguities. While we agree with the Bank of England’s stance that strong and predictable regulations are essential to reassure foreign investors, ensuring regulatory transparency and clarity for a sector that drives economic growth is equally important.
The BoE’s publication of the final Basel 3.1 rules and easing of capital requirements was a strong step in the right direction. However, uncertainty continues regarding the potential impacts on the UK of further changes and delays with the USA Basel Endgame. The industry will also benefit from more clarity in areas such as Solvency II, and the balancing act between Consumer Duty rules and the UK regulatory approach to innovation in areas like AI and digital assets.
Investment is negatively impacted by uncertainty. Financial services make up 8% of the UK’s GDP — it is important to ensure growth, competitiveness and innovation in Financial Services is supported in the right manner. We hope the budget will be taken as an opportunity to continue improving certainty, laying the foundation to drive more innovation and investment in the UK. Hopefully, the Chancellor’s Mansion House speech will provide this clear vision for the financial sector.
Peter Mardon, Corporate Solicitor and Director, WSP Solicitors
Well, the budget has been delivered. As expected, huge tax increases but also huge borrowing increases and huge spending increases. For businesses the increase in National Insurance will make it even more expensive to employ people. This increase in NI adds £25 billion extra tax on UK businesses.
But the government felt it needed to raise tax. However, its primary choice to target NI could be a bad choice as it is a “tax on jobs”
The Office of Budget Responsibility (OBR) says 75% of that additional NI cost will end up being borne by working people, which is almost £19bn. Do not think you are exempt because it is employer NI and not employee NI that has increased.
The increase in Capital Gains Tax rates was also expected and is perhaps less aggressive than many feared. However, there is still no indexation so it remains a tax on inflationary gains. We assume the increases will come into effect next tax year so we expect a rush by entrepreneurs to sell their businesses and other assets before then.
Certainly a historic Budget. The tax burden is now at 38% of GDP, an historical high. And yet, as always, the devil is in the detail which will emerge over the next few hours.
Rory McGwire, founder of Start Up Donut
This government appears committed to addressing the tough financial realities they’ve inherited, and for that, I commend them.
However, it’s ironic that the hardest-working segment in our country – families who run small businesses – are being hit the hardest by these ‘Make Work Pay’ changes. While I’m relieved the Employment Allowance offers some relief for the smallest businesses, who often struggle the most with covering their costs and complying with the seemingly endless rules on tax and employment, the recent focus on ‘protecting the workers’ has created a sense of a ‘them-and-us’ divide in this Budget.
Small businesses account for 48% of employment in the UK, yet this approach seems to pit employees against their employers. For many, the risks, workload, and challenges of running a small business may start to feel like they no longer match the limited rewards.
Charles McManus, chief executive of ClearBank, co-chair of the Innovate Finance Unicorn Council
The combined increase in capital gains tax and National Insurance – as well as the drop in the threshold for National Insurance Contributions for businesses – could have a significant knock-on effect in terms of the number of entrepreneurs establishing businesses in the UK, as well as already exacerbating the challenges we have already seen around UK businesses listing in other markets.
We acknowledge the challenging conditions this government is currently operating in. However, starting and scaling a business requires ingenuity, grit and determination – as well as taking a major risk – and we support any government that rewards that risk by creating an environment where entrepreneurs have access to the best investors, advice and scaling opportunities available.
Lily Megson, Policy Director, My Pension Expert
Even though drastic pension tax changes didn’t materialise in today’s Budget, the damage has already been done. Weeks of speculation and rumoured sweeping reforms left savers anxious, causing many to rethink carefully planned retirement strategies. For those already wrestling with financial difficulties, this added uncertainty will have only deepened concerns about their future security.
A confirmation of their already-pledged commitment to the triple lock and an increase in pension credit are welcome, if underwhelming. But it is not enough. The government now has an opportunity to rebuild that trust by focusing on initiatives that genuinely support savers. Finally prioritising comprehensive financial education and tools like the long-delayed pension dashboard will empower people to make informed decisions and feel confident in their retirement planning. What’s more, the second half of their pension review must deliver more than just lip service – savers need real, actionable reforms that encourage greater contributions and improve outcomes for retirement planning across the board.
A nod to either of these engagement-boosting policies would have been a welcome announcement that could have alleviated some of the pension tax raiding fears.
It’s now crucial that the Chancellor recognises the importance of stability and clarity in pension policy. Restoring confidence among savers will require transparent, considered policies that support long-term financial wellbeing, rather than fuelling rampant speculation that only undermines it.
Dan Olley, CEO, Hargreaves Lansdown
We recognise the difficult choices the government faced in today’s Budget and so it was clearly going to be mixed messages for the UK’s savers and investors.
Clearly, the Chancellor was listening when it comes to tax-free cash in pensions, and protecting those who have done the right thing, steadily investing in their retirement accounts to secure their financial future. Investing for later life is a long-term endeavour and so stability of policy is key if we want more people across the UK to benefit from the power of compounding to deliver a comfortable retirement.
It was also welcome that the potential consequences of dragging more people into higher income tax brackets through frozen thresholds was avoided. However, some of the other changes to inheritance tax and capital gains tax will be a disappointment for some.
We know from our own data on financial resilience that just one in five in the UK can expect a comfortable retirement, so as a nation we need to do everything possible to make it easy for people to save and invest.
Despite the gives and takes in today’s Budget, the most valuable investing tool we all have is time. The earlier you start, the greater benefit from compounding over time. Therefore, it’s vital that people don’t get distracted by today’s announcements or take this as a disincentive to continue to save and invest for the future.
With this budget behind us, I hope that this now provides the certainty, simplicity and stability required to give the retail investors across the country the conditions they need to keep investing and achieve their financial freedom.
Greg Pogonowski, Wealth Planner at Kingswood Group
The budget will affect the financial services sector in five key areas:
- Raising employers’ NI contributions by 1.2% to 15% from April 2025 is the big fiscal hitter of the budget – £25bn a year by the end of the parliament – and probably the most politically perilous choice Reeves has made.The government will also reduce the secondary threshold from £9,100 to £5,000. This will have implications on tax and investment planning leaving employers with less room for pay rises perhaps?
- Inheritance Tax. From April 2026, the first £1m of combined business and agricultural assets will not incur inheritance tax but after that it will apply at an effective rate of 20%. Farmers with assets over £1m will be subject to 20% inheritance tax above this amount. They were previously exempt. This will affect investors “using” farms as a means of avoiding IHT such as James Dyson and Jeremy Clarkson potentially.
- The rise in CGT was very much baked in with budget expectations, and the increases are not huge, but may impact fund managers as they might have fewer opportunities for tax-efficient investment planning.
- Private equity fund managers. Previously subject to capital gains at rates of 18% and 28%, the tax will be a single rate of 32% from April 2025. However, it is likely to rise further from April 2026 when it will be subject to a new regime. This could affect returns on funds.
- Largely unaffected apart from Inherited Plans, which is a good thing. More details to follow I suspect.
Craig Ritchie, Partner, GSB Wealth
Overall, the budget has not been as hard hitting on personal finances as perhaps expected, largely thanks to the increase in employers’ National Insurance. Increases to Capital Gains Tax are not as high as expected and level the playing field once more between shares/funds and property investing.
Inheritance Tax
It is good to have clarity on Inheritance Tax nil rate band (NRB) continued freeze, although this will bite as more estates fall into the IHT brackets. The exposure of inherited pensions to IHT will reduce the attractiveness of pensions as a wealth transfer tool, changing the landscape for pensions.
Bringing AIM stocks into the scope of IHT, even at a reduced rate, will have a negative impact on the value of smaller UK companies, decimating the viability of AIM as an IHT planning tool.
Abolition of Non-Doms Scheme
“The abolition of the non-domicile scheme and move to a residency based scheme presents huge opportunities for UK expats, who intend to remain outside of the UK to pass on wealth free of UK IHT. For those transitioning back to the UK, there is an opportunity to take advantage of the generous four-year foreign income and gains (FIG) regime. The increase in additional stamp duty will further weaken the landlord/buy-to-let investment market and support investment into other traditional investment vehicles. It is likely that we will see Scotland and Wales follow with increases to their stamp duties.
Matt Ryan, Chief Transformation Officer at Reef, Powered by Totem
Despite the near-constant influx of news about the promise of AI – including the head of OpenAI promising that an AI ‘super-intelligence’ may be ‘a few thousand days away’ – the UK government has already halted a planned £1.3bn investment in AI and related technologies.
However, the Autumn statement announced intentions to publish an Artificial Intelligence Opportunities Action Plan, that will set out a roadmap to capture the opportunities of AI to enhance growth and productivity and better deliver services for the public. Our hope is that this shines a spotlight on the industry and encourages investment.
The tech is already transforming the financial industry and has boundless opportunities to further enhance efficiency, personalisation, and security. However, it’s not just investment that’s needed to maximise the impact of AI technology, there’s a large body of work that needs to be done to educate businesses on best practice and how to ready itself – starting with building a volume and quality of data for this intelligence to work from. Just as you wouldn’t put custard in a Ferrari, there is no point adopting the latest AI if you haven’t got accurate and clean data to fuel it.
Before businesses run towards the latest AI technology, they should first be looking at how they can gather data in a way that is effective, efficient and transparent. Doing this will lay the foundation for the truly game-changing AI applications of the not-so-distant future.
Nimesh Shah, CEO, Blick Rothenberg
I have never seen such wild speculation on tax before a Budget announcement – but there were very few tax measures announced in Rachel Reeves very first Autumn Budget speech.
On Halloween eve, the new Chancellor took to the House of Commons stand and raised 94% of her £40bn target through an increase to employer’s National Insurance (‘NIC’) and a new repatriation facility for non-doms to remit overseas monies to the UK at a favourable 12% rate of tax for two tax years.
NIC threshold cut – the real tax raiser
The public headline from this Autumn Budget will be the £25bn employer’s NIC increase. From April 2025, employer’s NIC will increase by 1.2% to 15% (which is slightly lower than in 2022 when we had the 1.25% Health and Social Care Levy) – but the reduction to the threshold at which employers start paying NIC to £5,000 will be the real tax raiser, representing an additional cost of £615 per employee.
A business employing five people each earning £50,000 will face an increase to the NIC bill of over £5,500.
As widely rumoured, CGT was increased with immediate effect on 30 October – but the respective increases to 18% and 24% will be welcomed by entrepreneurs and investors who were fearing something much worse.
Whilst Rachel Reeves said she wanted ‘entrepreneurs to invest in their businesses’ and retain the £1m lifetime limit for ‘Business Asset Disposal Relief’, the tax saving will be worth a meagre £60,000 in April 2026 – a dramatic fall from grace from Entrepreneurs’ Relief which was worth up to £1m in 2020.
Private equity faces a 4% increase to 32% on capital gains on carried interest from April 2025; but the carried interest regime will be brought within the scope of income tax and NIC from April 2026, so it is more like a 6% increase.
Some non-doms were optimistic that the Government would go back to the drawing board on Jeremy Hunt’s Spring Budget announcements – but there was no such good news as the reforms are going ahead in largely the same form as previously announced.
Potential fiscal black hole
The only good news for non-doms is that the tax rate for the temporary repatriation facility is confirmed at 12% for 2025/26 and 2026/27, with the Government now projecting to raise £12.7bn from these refined measures. I expect many non-doms to carefully consider their future in the UK given the severe IHT impact of the reforms, which may dampen the additional tax revenue the Government expects to raise. Fiscal black hole anyone?
Family businesses will be scratching their heads around what to do given the cap to Business Property Relief of £1m and a 50% discount thereafter – but they have until April 2026 to work something out (but they will need to watch out for some anti-forestalling measures for lifetime transfers made from today).
So, the Autumn Budget may not have been as scary as expected…but the Prime Minister and the Chancellor are not ruling out more tax frights in the Spring.”
Gary Smith, Financial Planning Partner and retirement specialist, Evelyn Partners
Pensions have been one of the most tax-efficient investments available to savers, with tax relief on personal contributions, tax-free growth and pension funds remaining outside of your estate for IHT on death. That means some retirees have prioritised using other savings and assets to fund retirement before their pensions.
More details are to follow, but the Chancellor has removed the IHT-free status of defined contribution pensions from April 2027, which will mean that the proportion of estates subject to IHT will grow from the current 6%.
Retirees and savers have 18 months to review their long-term plans. As defined contribution pension funds could now be subject to up to 40% IHT on death, we will probably see greater withdrawals from pension pots.
Pension withdrawals are subject to income tax, so some savers in drawdown will have an eye on the frozen £50,270 threshold at which point their overall income from all sources will be taxed at 40%.
It’s arguable that this consolidates the two tiers of the UK pension system, as the change removes one of the few advantages that defined contribution pensions had over the gold-plated final salary schemes that now exist largely just in the public sector. DC pot holders could leave their savings to beneficiaries tax-efficiently, while the death benefits for members of public sector or defined benefit pension arrangements vary between schemes, but usually entail an income paid to dependents.
There seems to be a willingness in Whitehall to allow the gap between private and public sector pension arrangements to widen.
Annette Spencer, Chief Executive, Association of Corporate Treasurers
After a number of years of economic uncertainty, this budget provided an opportunity for the government to deliver clarity, predictability and confidence for corporates so that they may be better positioned to contribute towards UK growth.
Treasurers (the financial risk managers in any organisation) prefer to work in an environment where there is as much certainty as possible, especially around funding availability and access to talent, and today’s announcements – if they are supported by achievable goals – are a positive step to facilitating this.
Some measures to be welcomed
On that basis, we welcome a number of the measures announced today including the road map for corporate taxation and the specific pledges to cap corporation tax at 25%, and to maintaining the full expenses system of capital allowances for the rest of this Parliament.
We also welcome recent commitments made to consult on a new Industrial Strategy. This should encourage investment and help treasurers address funding new rounds of capital expenditure.
The Chancellor also confirmed changes to the fiscal rules and the treatment of debt on capital investment. While considerations will need to be made around value for money for taxpayers, measures to improve public services and infrastructure that improve productivity and ultimately support business are certainly welcome.
Other measures potentially will negatively impact business
However, a number of proposed changes will have significant negative impact upon business in the UK, notably the increases in NICs for businesses and CGT allowances. While any increase in business taxes is unpopular, it is the unintended consequences of such decisions that are most concerning. Such changes will likely cause disruption among the business community – and be particularly challenging for smaller companies who, given their pivotal role in many supply chains, are key to the long-term success of the economy. These smaller businesses are already managing tighter working capital alongside higher funding costs, and we hope that the unintended consequences of today’s announcement are not the final straw.
While the Chancellor did outline measures to help reduce costs for smaller businesses, overall, we believe there was a missed opportunity to do more on funding capabilities. Access to funding is an important issue for helping smaller businesses grow, but we do need opportunities to encourage lending, too. Areas such as sustainable finance and digitisation are huge growth areas and we’d hoped the Chancellor would have looked at these areas.
Susannah Streeter, head of money and markets, Hargreaves Lansdown
The cloud of confusion hovering over retail investors has lifted with the government holding off from tinkering with ISAs. The Budget announced that ISA, LISA and JISA allowances would stay frozen until 2030. This should help maintain confidence in what is the cornerstone for retail investment in the UK. UK retail investors are enthusiastic holders of UK equities, at HL around 35% of our clients hold UK equities directly with 75% of trades by value taking place on the London market. Maintaining tax free allowances will encourage greater long-term investing and saving and but other nudges are also needed to help encourage more people to take the first steps on their stock market journey.
UK ISA plans axed
It’s a relief to see plans for a UK ISA dumped on the scrapheap. It was a well-intentioned idea but was set to lead to unfortunate consequences. The plan was to direct shareholders money into UK-listed companies, but such a move would have added unnecessary complexity and could have a negative impact on UK investors. If they had been nudged into a UK ISA, it would have potentially increased risk by unnecessarily concentrating portfolios. This could be a detriment, especially if there was more volatility in the London markets compared to others. For some people, the complexity may have put them off putting money into equities, given that simplicity is what many investors desire.
Small-cap market: blow to investors
The reduction of tax breaks on AIM quoted stocks is a blow for investors in the small-cap market, and although some have clawed back losses given the business property relief was not completely scrapped, trading is likely to remain volatile. Investing in such companies, given how fledgling some are, is a risk, and some investors might have been prepared to take given that IHT wasn’t due on such portfolios as long as they had been held for two years or more. There could be longer-term economic implications here given that this small change might have big repercussions when it comes to creating a nurturing environment for entrepreneurial businesses, which may be counter-productive to the Chancellor’s growth agenda.
CGT changes: backward step
The changing CGT landscape creates uncertainty, with wealthier investors, who have maxed out their ISA allowances, now facing increased tax on equity gains. However, the hike to 24% was not as high as many feared it could be. Ultimately this move is a backwards step and may prompt investors to take profits bit by bit by using their allowances to realise gains and parking this money elsewhere.
The UK market is an income king, and enjoys the highest dividend yields among its peers, including the S&P, DAX, CAC 40. But these benefits are being swallowed up by the low level of the dividend tax allowance, which had already been slashed from £5 thousand in 2016, to £500 pounds. The chance has been lost to incentivise investment by increasing this allowance, especially given the government says it wants to encourage investment in UK assets.
The UK remains out of line with other leading nations in the world, given that the stamp duty payable on shares listed in London will remain the highest in the G7. It’s illogical for investors buying UK shares to have to pay our high stamp duty when overseas trades have a lower rate or are stamp duty-free. It means the playing field for UK plc remains uneven, which may hold back vital funds for British based companies hoping to grow, given that the 0.5% tax will still be payable by investors.
The Chancellor made a series of announcements about her National Wealth Fund. While it has lofty ambitions to attract inward investment from the big beasts of global finance, opportunities need to be created for armies of smaller retail investors, who together would be a significant force for good in helping boost growth. Opportunities to invest in growth companies are few and far between with retail investors left out of most the stock market flotations. As plans for the Fund develop, we look forward to building out opportunities for retail investors.
Darren Upson, VP of Europe, Tipalti
While the increase in capital gains tax is not as high as originally feared, it still raises concerns for entrepreneurship in the UK, the attraction and retention of talent, and risks dampening investor confidence.
However, the UK remains a hub of exceptional talent and innovation. To thrive and maintain our status as a global fintech leader, businesses must focus on what they can control.
Knowledge is power and having the right data at your fingertips to make informed decisions is crucial. Working within tighter budgets, businesses need agility and foresight to spot opportunities as they arise to maintain a competitive edge. With the right finance technology, UK businesses can position themselves for long-term success, regardless of the current fiscal landscape.
Pino Vallejo, CEO of Davies Consulting
As expected, it was a bumper Budget. Indeed, it was always likely to be a crucial Budget from the Chancellor, given it was the first major fiscal statement under the new Labour government – its first in 14 years.
Reeves’ speech was filled with a vast number of significant policies, reforms and spending commitments. The challenge for businesses is to take time to fully digest each element of the Budget and, in turn, understand the implications of the proposed changes; not just on their business but, crucially, on their customers.
This is especially true for financial services firms. This Budget will have a notable impact on the finances of both consumers and businesses, so the financial services industry must respond accordingly, ensuring they evolve with the political and economic climate and deliver the best possible service to customer.
Tiago Veiga, CEO, Aurum Solutions
Hiking the rate of capital gains tax is counterintuitive to the UK’s ambition of becoming an established global hub for technological innovation and fintech. What we need to be doing is creating an environment that enables businesses to generate wealth, and incentivise growth, not the opposite.
The onus is now on entrepreneurs to drive even greater growth, so they can reap the same rewards. To do so, businesses should focus on proactively finding the tools they need to scale sustainably, and this starts with enlisting time and cost-saving solutions. Technology like automation can free up an enormous amount of resources for businesses to spend on revenue-generating activities, particularly for startups who may already have limited capacity. Against a backdrop of greater tax burdens, this will be key to business prosperity in the long run.
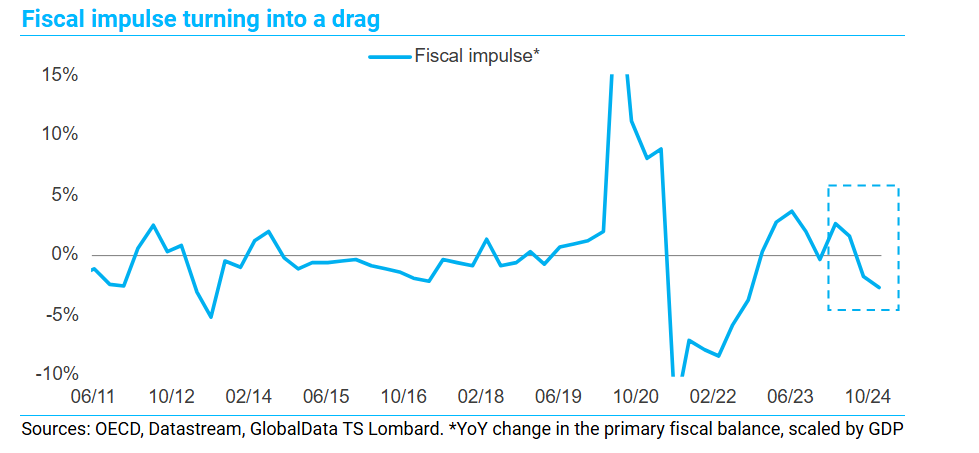
Konstantinos Venetis, Director, Global Macro, GlobalData TS Lombard
Chancellor Reeves faces a tough task striking a balance between three overlapping objectives.
First, boosting public investment, a prerequisite for raising the economy’s speed limit. Second, tackling deficiencies in spending on public services, which will inevitably imply increases in taxation. Third, sending the right signals on debt policy, i.e., revamping existing rules while providing reassurance about the prudent stance on borrowing being maintained.
Need for (fiscal) space.
The devil is always in the detail, but we expect the chancellor to open up fiscal space by carving out public investment from the deficit rule (i.e., public sector borrowing should not exceed 3% of GDP in five years’ time) and to tweak the definition of debt used for the fiscal rule (i.e., debt as a share of GDP on a falling path over a five-year horizon) in order to increase the budgetary “headroom”. As the chancellor said recently, “We have to make sure we unlock that space for capital investment…I hope that at the Budget the OBR will look at not just the short-term impact of boosting capital investment but also the long-term impact and the catalytic impact of public sector investment crowding in private investment.
Arjan Verbeek, CEO of Perenna
The government’s home building targets are admirable, and we applaud their ambition, however the measures announced today, including the plans to make the Mortgage Guarantee Scheme permanent, barely move the dial on increasing homeownership.
The maths is simple. The average UK salary is around £35k, and the average new build is around £300k. Under current rules, only 15% of lending can be above the four and a half loan-to-income (LTI) cap, which restricts mortgage financing capacity to £23bn. So even with a 5% or 10% deposit, the person looking for an average house would be off by £100k. This needs to be fixed.
To deliver 300,000 new homes a year for aspiring homeowners, the market needs to provide £85bn in annual mortgage financing. The government needs to change outdated regulations that are hindering growth like the LTI cap. Low-risk mortgage solutions, such as long-term fixed rate mortgages minimise the risk the LTI cap is concerned with, bare no burden on public finances, and therefore should be exempted. The cap was introduced as a way to prevent risk, but it is now preventing homeownership. We need to change this urgently so we can become a nation of homeowners again.
Gilbert Verdian, Founder, CEO, Quant
The imagined ‘mass entrepreneur exodus’ makes for a good headline, but it is more rhetoric than reality. There are many, many more of us entrepreneurs who are committed to staying put and paying our fair share. Nowhere else can match London when it comes to talent, capital raising, and stable regulation. These advantages have been built up over centuries of competitiveness and innovation and – regardless of tax tweaks – are here to stay.
It may be painful in the short-term, but this is the budget we need to have. We need to remember that in the long run, this will increase government investment in large infrastructure projects and public services, boosting the health of the whole economy. Ultimately, the Budget can be seen as a catalyst for future growth.
Jason Whyte, Financial services expert, PA Consulting
Despite widespread expectations of reform to pensions tax relief, the Chancellor only revealed one major change in her speech.
Inherited pension wealth will now be included in the scope of Inheritance Tax (IHT) from 2027. This addresses an anomaly in how pensions have been treated relative to other wealth – around 8% of estates include pensions that until this change were exempt from IHT. More widely, pension savers and their advisors will be breathing a sigh of, well, relief that there were no changes to pensions tax relief or a cut to the pensions commencement lump sum (popularly known as “tax free cash”).
There could be a flurry of activity to undo pensions transactions in the wake of the Budget.
There was a widespread expectation of changes to allowances on pensions and financial advisors reported customers crystallising their pensions early to lock in tax free cash at pre-Budget levels. But the Chancellor did not introduce any changes – so pension providers may be receiving requests to undo those transactions or cancel any that were set to take effect later.”
The State Pension Triple Lock remains until 2029.
The Chancellor committed to maintain the Triple Lock through to 2029, with pensions set to rise at 4.1% compared to inflation of 2.5% next year. That will see State Pension spending reach £31bn by 2029. The Triple Lock is a popular measure and Chancellors have faced significant backlash for trying to change it – but it guarantees that a major area of Government spending will grow at least as fast as inflation. It will eventually need to be reformed, but that has perhaps been left to a future Chancellor.”
The Chancellor has launched a Pensions Investment Review that is likely to encourage more public-private investment in UK infrastructure and growth-driving sectors.
Final salary pensions have historically been big investors in infrastructure and other long-term projects. But defined contribution schemes often feel that they cannot invest significant amounts in illiquid investments, while also meeting regulatory requirements to offer customers easy switching between funds. The pensions review is likely to listen to providers’ concerns and make investment in long-term assets easier.
Subscription limits for ISAs have been frozen until 2030
This means that savers can shelter a smaller proportion of their savings in real terms from CGT and income tax. While this has a relatively small impact in the early years, it is forecast to increase the tax take by £605m in 2030. The previous Government’s proposed British ISA is also scrapped.”
The government has indicated that digital innovation, including the Digital Information and Smart Data (DISD) Bill, is a priority.
DISD will provide the primary legislation to expand Open Banking into a wider Open Finance and Open Data regime. But it remains to be seen how quickly it will move – and whether it will provide the incentive needed for the industry to deliver the consumer innovation and value that the government and regulators want.
Ryta Zasiekina, co-founder, CONCRYT
With a booming tech industry and so many innovative startups, it was easy to see why in the Spring Budget, former Chancellor of the Exchequer, Jeremy Hunt, claimed the UK was “on track to become the world’s next Silicon Valley.
Fast-forward to the Autumn Budget statement, and we have a new Chancellor and seemingly a new set of priorities that the fintech industry is notably absent from. While it declared ambitious plans for innovation and growth, one glaring question remains: what happened to those lofty aspirations outlined in Spring?
Only this month, a group of UK fintechs reportedly met with the government, concerned about growth limits. At that meeting, Bloomberg reported that representatives from companies including Revolut, Clearbank and Zilch warned City Minister Tulip Siddiq that Great Britain could fall behind in the fintech space if the government neglects key industry concerns.
Despite investment in technology and fintech, the UK continues to face barriers that hinder its ability to compete with global innovation hubs. For the UK to become the next tech superpower, we need to see investment in the infrastructure required to support industry growth.
From a lack of long-term government support to talent retention challenges, the vision of creating a thriving tech ecosystem that rivals Silicon Valley remains elusive. I question if the current strategy is enough to truly position the UK as a leader in the global technology race. If this Autumn’s statement is anything to go by, more decisive and bold action is needed to make that ‘Silicon Valley’ vision a reality.
Andrew Burman, Principal, Tax Transformation and Automation at Ryan
Smart investments into HMRC are long overdue. The constant delays that taxpayers and advisers face every day are the result of outdated IT infrastructure and overwhelmed teams.
This is not through a lack of funding. We’ve watched the government pour plenty of money into HMRC in the past, but they’ve not been able to make the best of their IT investments as each part of the organisation relies on standalone, siloed systems. As a result, the UK is well behind many other tax authorities when it comes to the effective use of IT.
Fresh investment into HMRC is long overdue
This new investment should focus on automation and large volume data testing. The challenge, however, is that this will require significant training to deliver properly. New ‘data savvy’ teams may be hired by HMRC specifically for this purpose.
From a taxpayer perspective, this is a clear reminder that doing nothing in terms of data management and more real-time interrogation is no longer an option. In order to keep pace with current and future HMRC initiatives, the need to know your data and understand what it says before you share it, has never been more important.
Rob Straathof, CEO of Liberis
Banks have too often left small businesses behind, and now they may feel that the Chancellor’s new policies are doing the same. The government’s trifecta of changes will likely have a negative impact on many small businesses, which generate three-fifths of private sector employment and constitute 99.2% of UK businesses. As a result of these changes, small businesses will have less access to cash, meaning less opportunity to invest in stock and recruit, or even maintain staff.
Employer National Insurance changes and reduction in employment allowance will cripple SMEs
To avoid closures or job losses caused by these policy changes, the government should reconsider the reduction at which employers start paying National Insurance and instead increase it to align with inflation. In these times when small businesses face increased obstacles, fintechs must step in.







