By 2020, the more technologically savvy generations, Millennial and Gen Z, will represent a significantly larger share of wealth preferring to avoid time consuming trips to physical branches when similar solutions are available.
The new financial services customer’s decisions are based on convenience (customer centric financial service provision). The new customer is digitally connected, highly informed and demands a highly personalized approach in his or her communications, products and service (this is a widespread industry term.) At a time when everything around us is becoming more complex, consumers are searching out those products and companies that can simplify our lives. The new customers expect individualised services that are tailored to them. Their trust is given based on receiving honest offers that are in line with a shared value system.
These customers are more sympathetic to the trusted services providers who they share a common value system rather that the benefits rating. They demand secured service anytime, anywhere, anyhow. Instead of walking into a local branch (branch agnostic customers) office, these customers purchase their banking services similar to how they purchase music, books or other products, 24/7. The frame of reference for these customers is not other financial institutions, but the best retailers and social marketers.
Increasingly also, the concern about financial inclusion divide is more apparent since most of the financial services providers segment and avoid certain sections of the population and consider them unviable. With the introduction of new technologies and as internet connectivity is availed more universally there is need to redevelop new strategies that can bring these previously ignored populations in to financial viability. The biggest impediments to financial inclusion is the accessibility of the financial services provider’s points of interaction. The last mile (distance from the client to the nearest financial service point) factors include the cost of travel, the time spent on the travel, the risks during the travel, and the time spent waiting in queues.
According to the World Bank group financial inclusion means offering financial intermediation, insurance, credit and savings services responsively and sustainably in a well-regulated environment. In order to properly deal with the elephant blocking access to full inclusion agency banking need to overcome the four critical financial exclusion factors i.e. cost, barriers to entry, information and last mile access. Our agency banking solution is in constant evolution to help deal with financial exclusion factors.
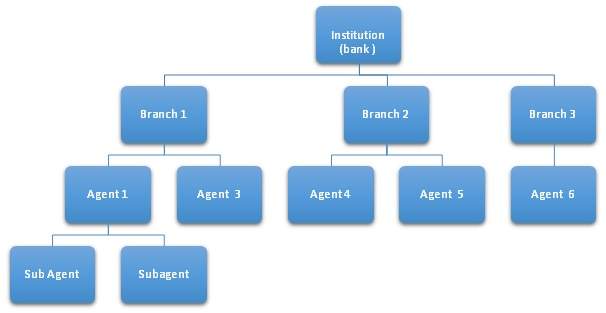
Branchless Agency Banking (BAB) is the Provision of financial services through a third party entity (Agent) to customers on behalf of a licensed, prudentially regulated financial institution, such as a bank or other deposit taking institution. Branchless Agency Banking forms a powerful tool to bridge the last mile factors. An Agent is one authorized to offer financial services on behalf of or represent a licensed, prudentially regulated financial institution (principal). They are independent entities bound to the principal by contractual obligations.

